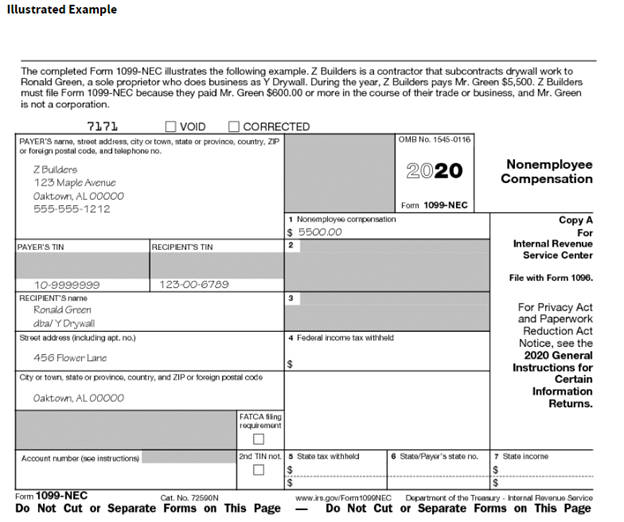
Beginning for tax year 2020, business taxpayers must report nonemployee compensation using the 1099-NEC Form. Prior to 2020, payers completed form 1099-MISC to report nonemployee compensation of $600 or more in box 7. Form 1099-MISC has been redesigned and no longer includes employee compensation. Instead, the IRS reintroduced form 1099-NEC to simplify the deadline among other things.
The 1099-NEC Form shown at right reports the payments made to non-employees on box 1.
Who must file Form 1099-NEC?
If the following four conditions are met, you must generally report a payment as NEC.
- You made the payment to someone who is not your employee.
- You made the payment for services in the course of your trade or business (including government agencies and nonprofit organizations).
- You made the payment to an individual, partnership, estate, or, in some cases, a corporation.
- You made payments to the payee of at least $600 during the year
If any amount of money was withheld for federal or state taxes, Form 1099-NEC must be filed.
Use Form 1099-NEC to report nonemployee compensation of $600 or more including
- Fees
- Commissions
- Prizes and Awards
- Other forms of compensation for services
- Fish purchases for cash
When is Form 1099-NEC due?
1099-NEC forms must generally be distributed and/or postmarked to recipients and the IRS by January 31. Since January 31 falls on a Sunday for the 2021 year, the 2020 forms are due the following day February 1.
There is no automatic 30-day extension to file form 1099-NEC. However, certain taxpayers may request one for specific limited reasons.
When do I have to file form 1099-MISC?
From 1099-MISC is still required for some business taxpayers. The major redesign in the form included shifting nonemployee compensation in box 7 to form 1099-NEC. Instead Box 7, shows if the payer made direct sales of $5,000 or more of consumer products to a buyer (recipient) for resale.
Business taxpayers should report payments made of $600 or more including
- Royalties ($10 amount or more needs to be reported)
- Rents
- Other Income
- Fishing boat proceeds
- Medical and healthcare payments
- Crop insurance proceeds
- Payments to an attorney
- Section 409A deferrals
- Nonqualified deferred compensation